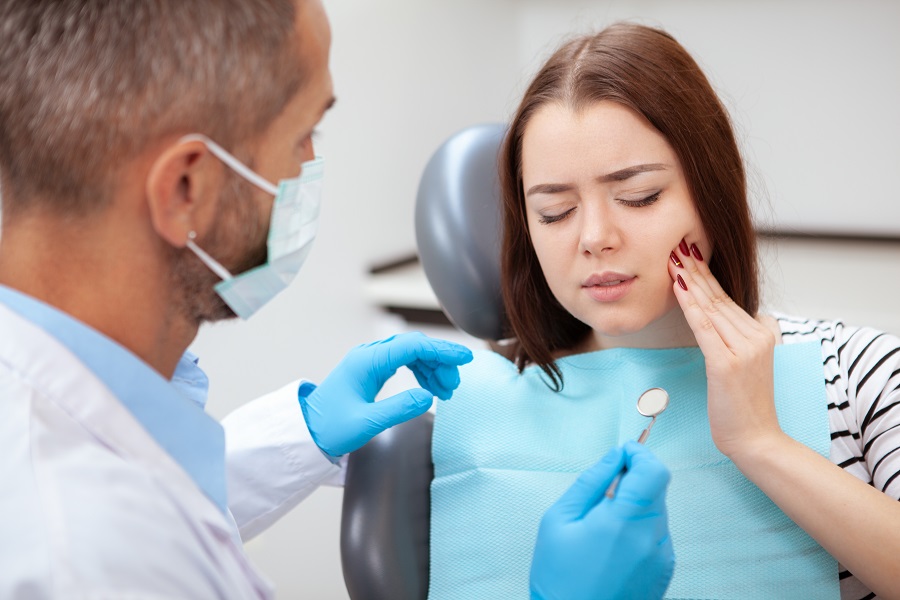
Periodontal Treatment
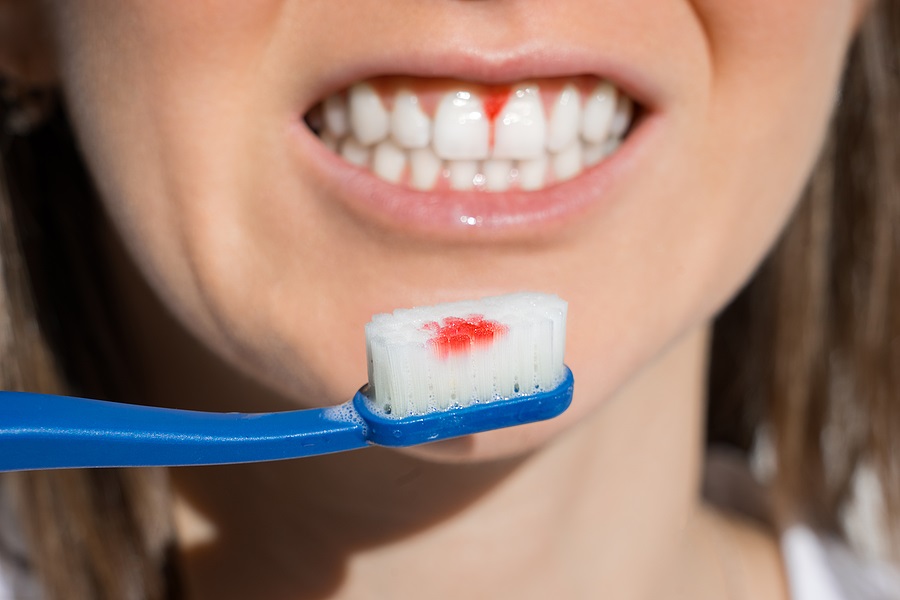
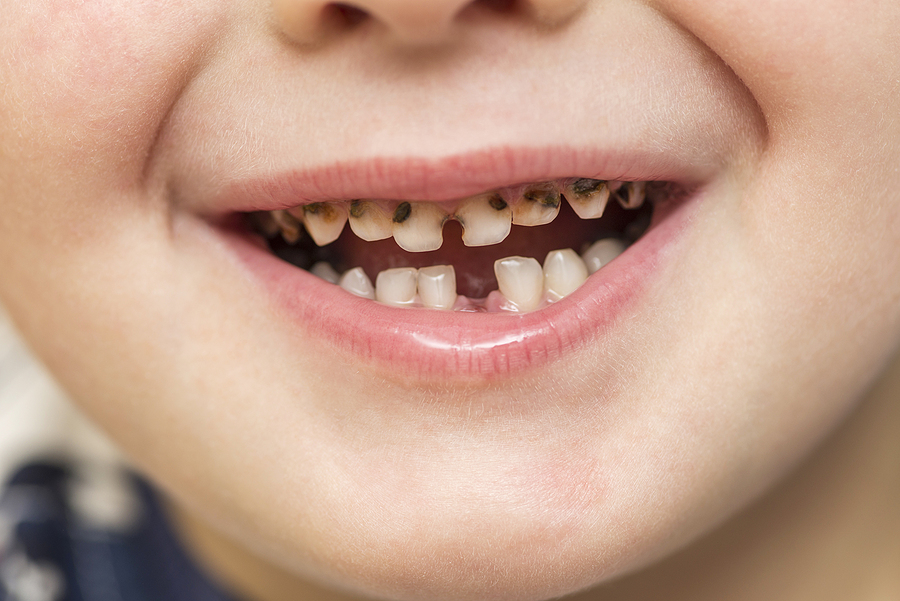
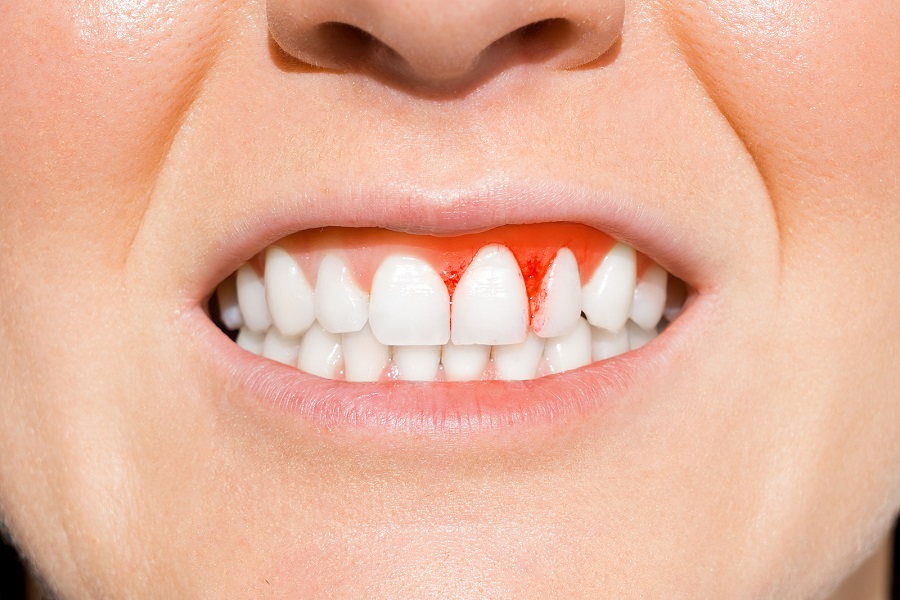
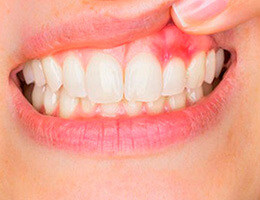
Periodontal disease, commonly termed gum disease, infects the soft dental tissues that hold the teeth in place, inflaming them in the process. This is followed by reddening and bleeding gums.
There are four stages of periodontal disease. The most common ones are gingivitis in an early stage and periodontitis when matured. In later phases, the gums recede from the teeth, loosening them from their structure. Eventually, this leads to tooth loss. If not treated soon, periodontal disease can lead to several other health problems.
What are the Causes of Periodontal Disease?
Due to poorly maintained oral hygiene, plaque - a sticky bacterial film, is formed on the teeth. This bacterial growth extends below the gum line contaminating the gums. As a result, gaps, known as periodontal pockets, are formed between the teeth and gums. These gaps flourish the bacterial growth, and they multiply faster, weakening the base of the teeth and breaking them from the supporting bone. Certain genetic and risk factors such as smoking boost up the whole process.
Symptoms and Signs of Periodontal Disease
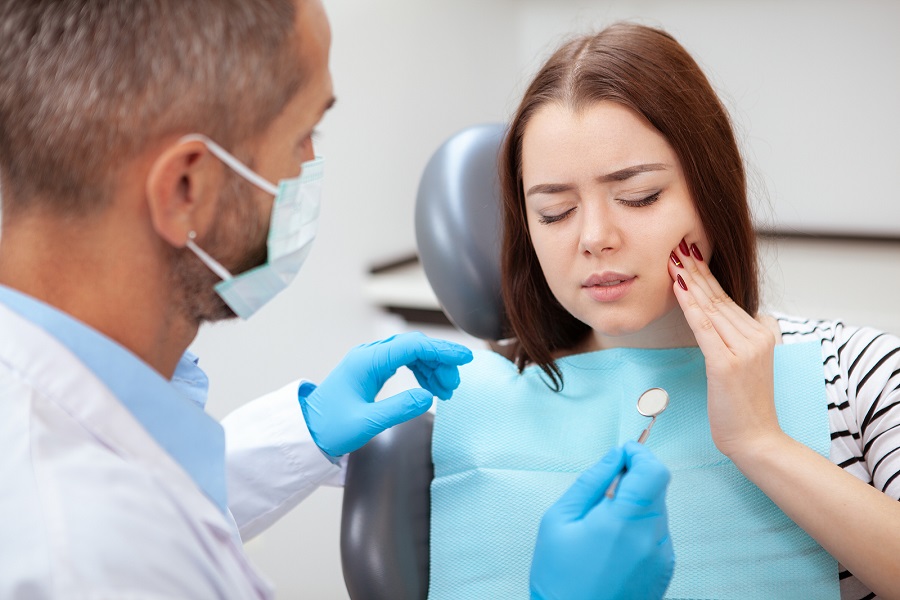
The first sign is bleeding gums whenever brushed. If not treated at the earliest, the symptoms may follow:
- Increased and impulsive bleeding of the gums
- Persistent bad breath and taste
- Receding gums
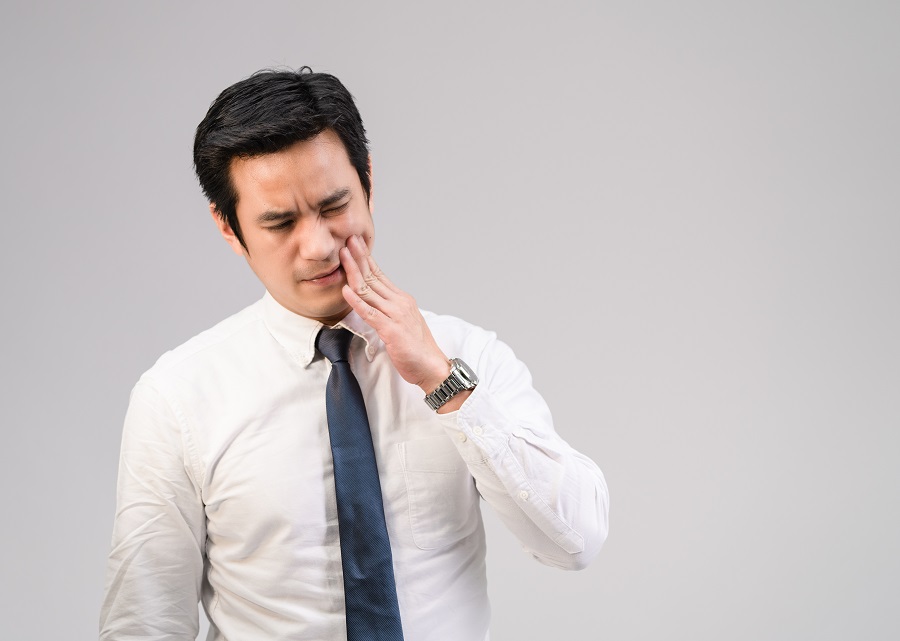
- Persistent pain in the gums
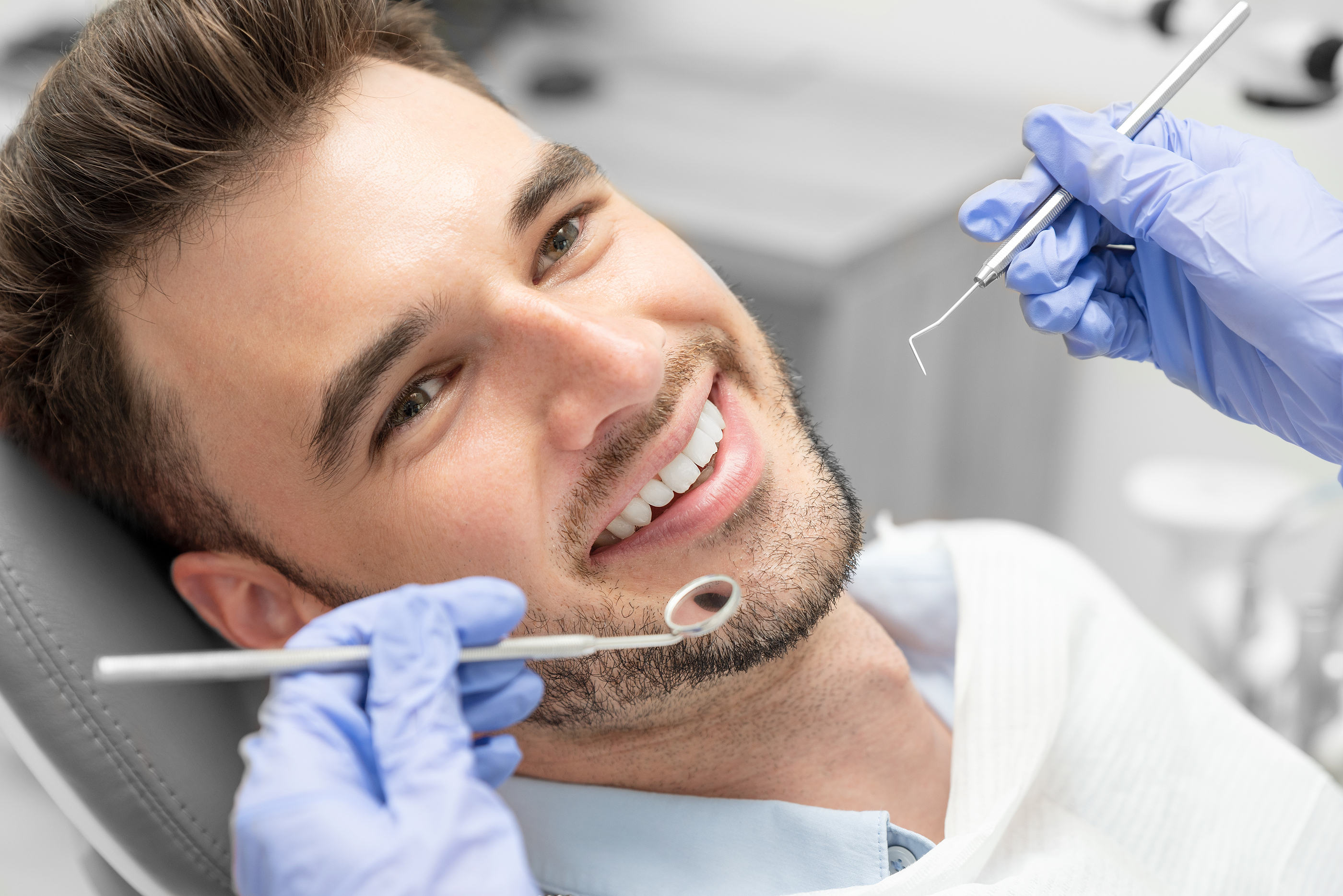
Treatment of Periodontal Disease
- In the first appointment, your dentist will explain the causes of periodontitis and give instructions to take care of your teeth and gums.
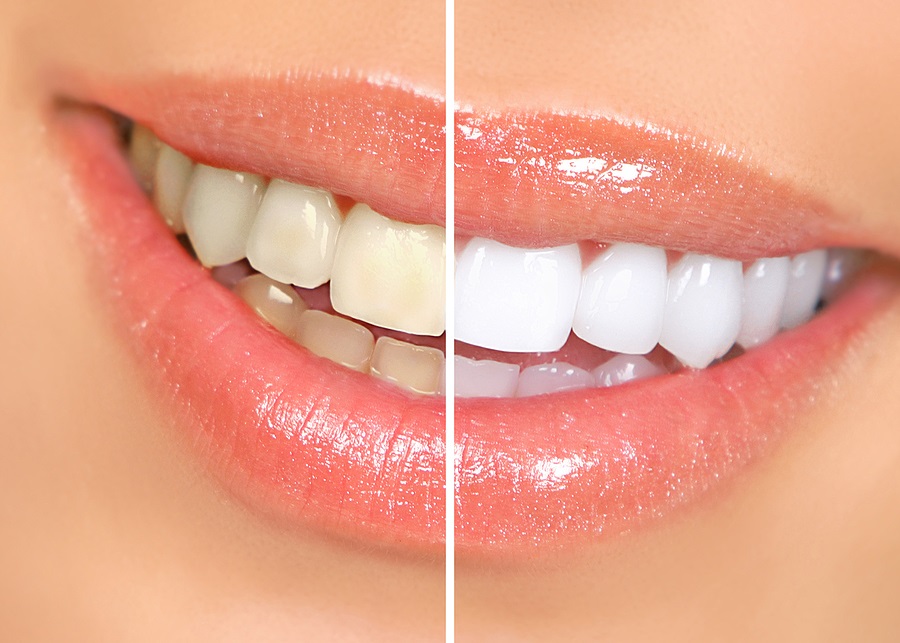
- After this, you go through a professional cleaning session to get rid of the hardened plaque. Normal brushing cannot remove the bacterial deposits from the gum pockets. The teeth will be treated with fluoride using a topical fluoride applicant.
- Some gum infections need more than oral hygiene treatment. In cases such as these, antibiotics are prescribed.
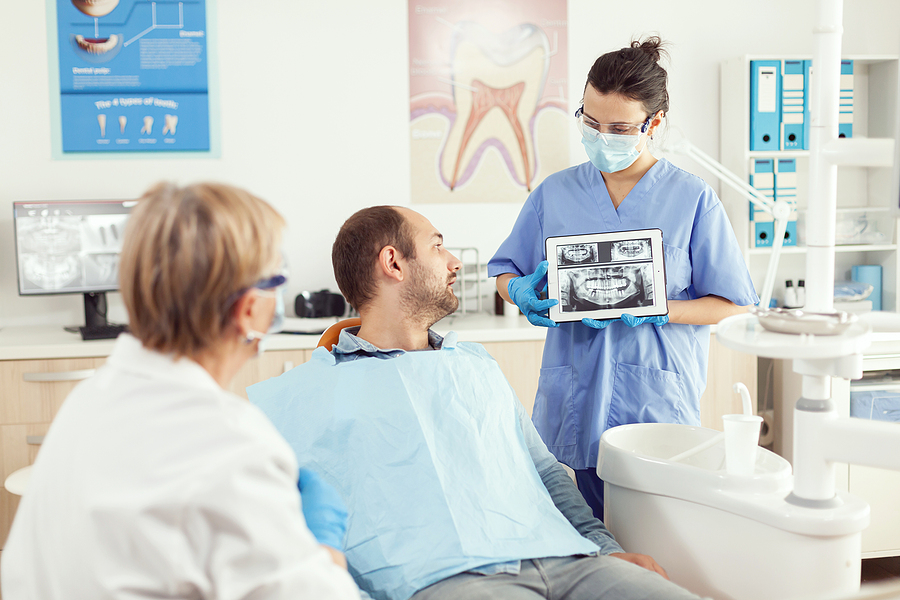
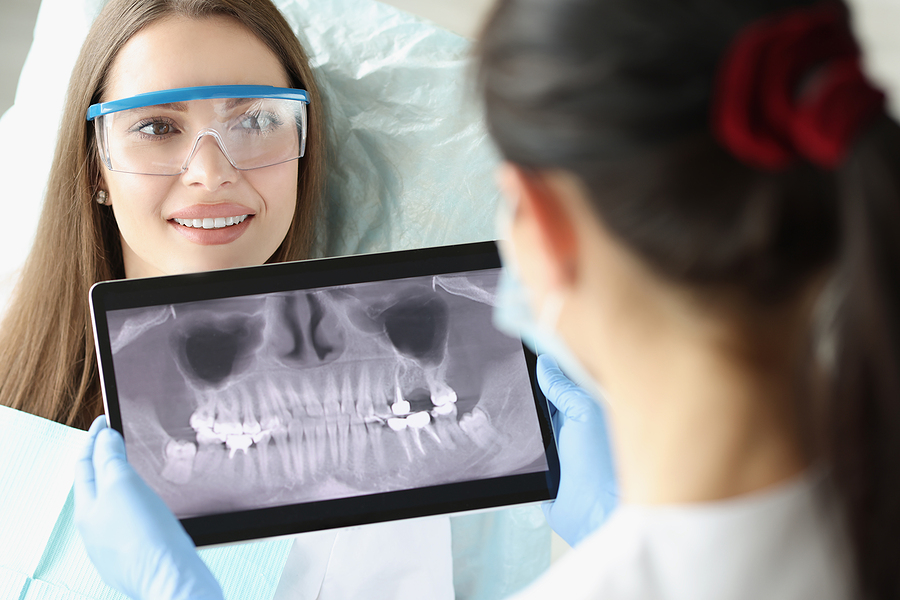
- After a few weeks, the dentist checks for bleeding gums and the depth of the gum pockets with the help of dental probes.
- If the depth is more than 3mm, bacterial growth and deposits are removed via surgery. After administering local anesthesia, the gum is elevated using dental instruments, and the root surfaces are cleaned. Using a special regenerative treatment, the bone at the roots is regrown.
Aftercare Guidelines
For the periodontal treatment to last longer, personal oral hygiene has to be maintained along with regular visits to the dentist. Toothpaste and mouthwash should be used as recommended by the dentist. In the follow-up schedules with the dentist, the inflammation of the gums is checked, and likewise, aftercare is suggested. The aftercare varies from person to person on the basis of the severity of the infection.
Please reach out to Persimmon Dental Care in Dublin, CA, to have a consultation with our dentists. Please call us at (925) 999-8282 or schedule an online consultation, and we’ll guide you further.
Periodontal diagnosis
Sedation Dentistry
Laser Dentistry

Early Orthodontic Treatment

What’s the Best Toothpaste for My Child?
Sealing Out Tooth Decay

Good Diet
How can fluoride prevent tooth decay?

Care for Your Child’s Teeth

First Visit

How Often Should Children Have Dental Checkups?
When Should Children Have Their First Dental Visit?
Office Hours
MON - FRI 9:00 am - 6:00 pm
SAT - SUN Closed