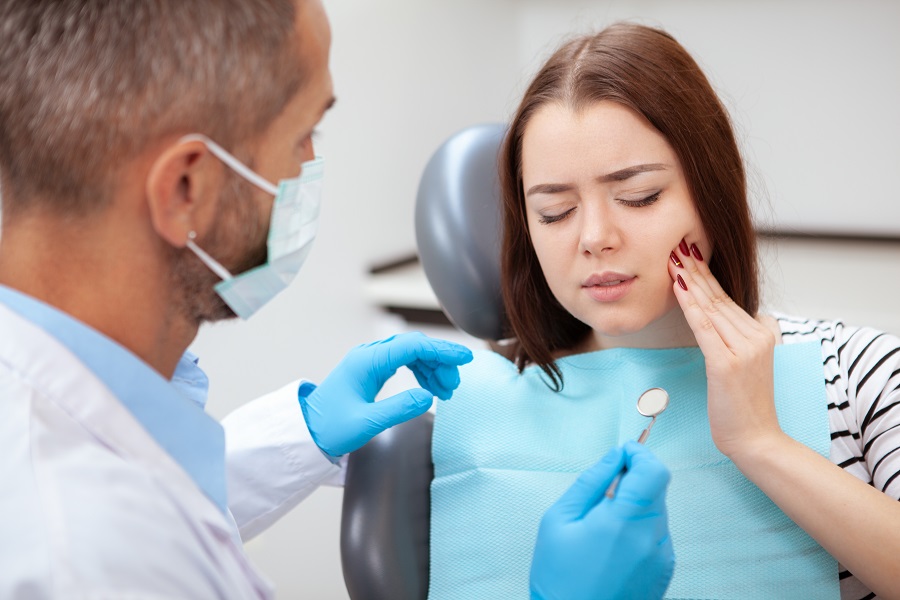
Gum Disease
Periodontitis, also known as gum disease, begins with bacterial development in your mouth and can lead to tooth loss due to damage to the tissue that surrounds your teeth if not treated appropriately.
Periodontitis (gum disease) is commonly preceded by gingivitis (gum irritation). Gingivitis does not always lead to periodontitis. Gingivitis affects many people at some point in their life, and its mild symptoms make it easy to overlook. You can avoid or even reverse it by brushing your teeth, flossing, and getting regular dental cleanings and checkups.
What Causes Gum Disease?
Gum disease is caused mostly by plaque. Other factors, however, can have a role in periodontal disease. These are some of them:
- Hormonal changes make the gums more sensitive, making gingivitis more likely to develop.
- Gum disease can be caused by a variety of illnesses. This includes disorders that affect the immune system, such as cancer or HIV. Patients with diabetes are at a higher risk of infection since the disease inhibits the body's ability to use blood sugar.
- Some medications reduce saliva flow, which protects teeth and gums.
- Smoking makes it more difficult for gum tissue to regenerate itself.
- Gingivitis is made simpler by poor oral hygiene habits such as not brushing and flossing daily.
- A family history of dental disease could be a factor.
What are the Symptoms?
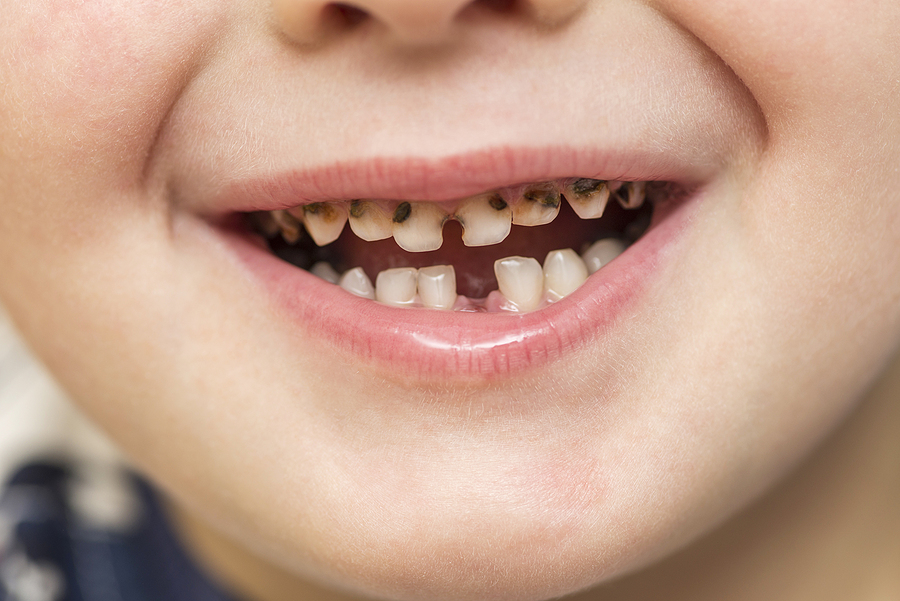
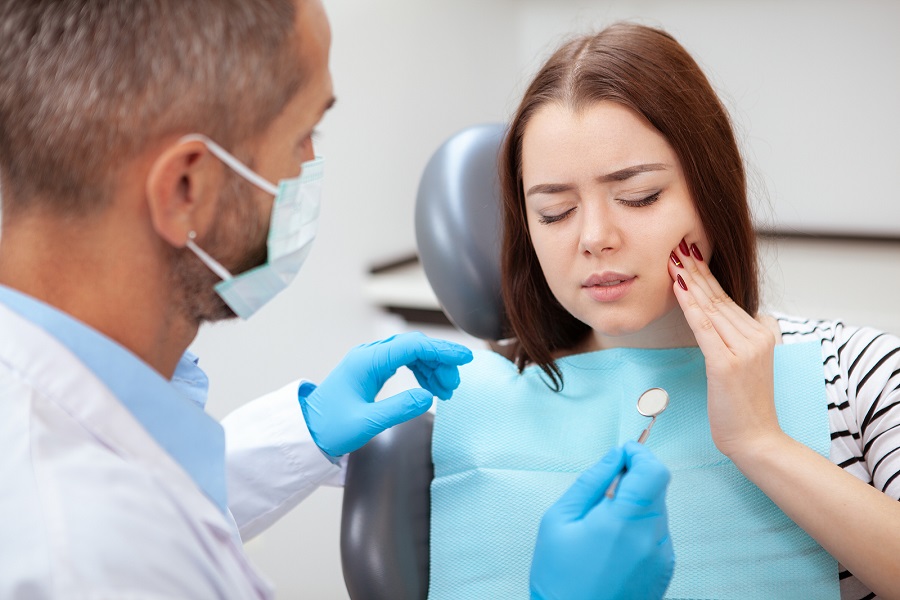
- Loose teeth
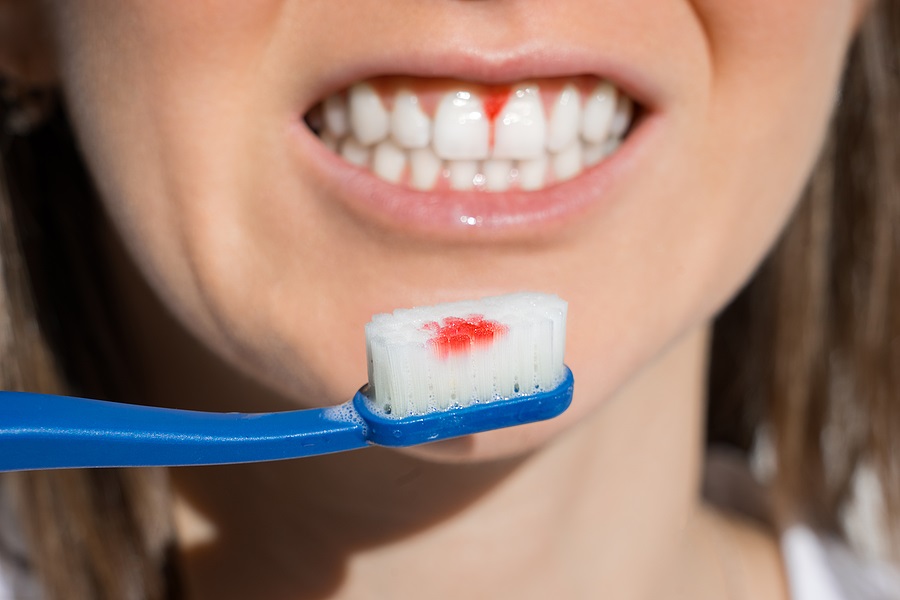
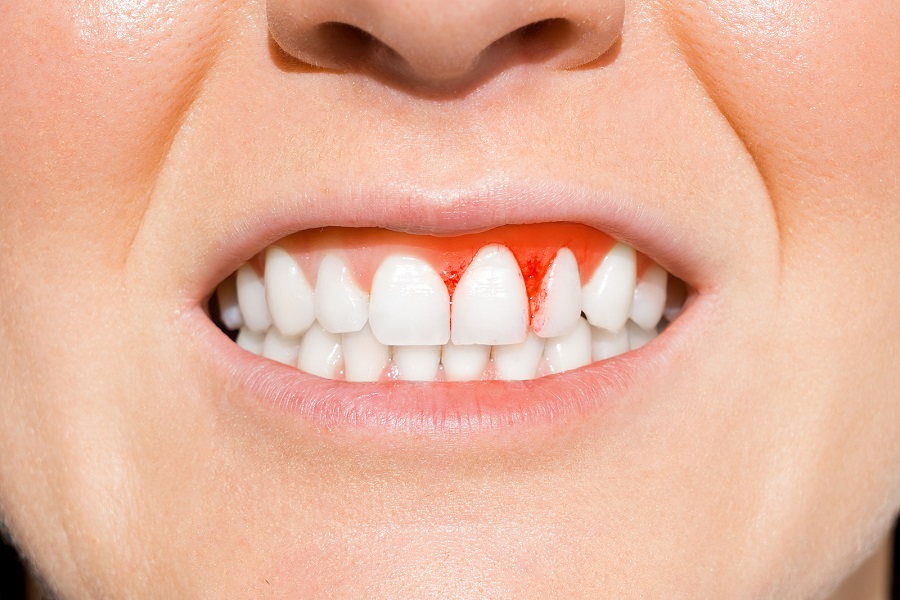
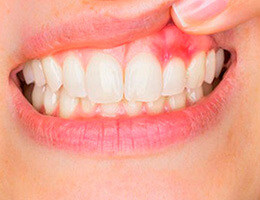
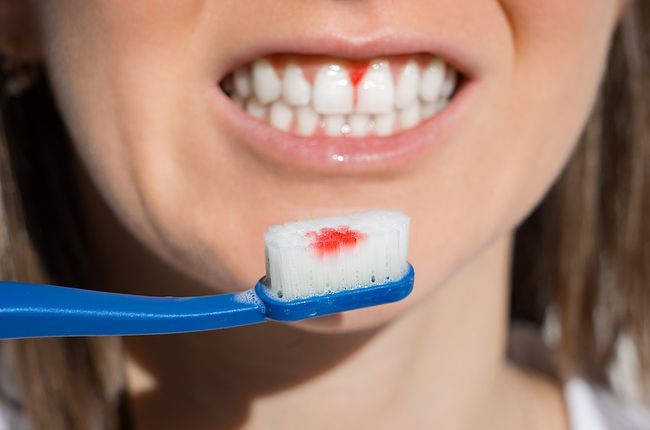
- Bleeding gums
- Red and swollen gums
- Bad taste in the mouth
- Bad breath
- Pus release from gums
- Tooth discoloration
- Receding gum line
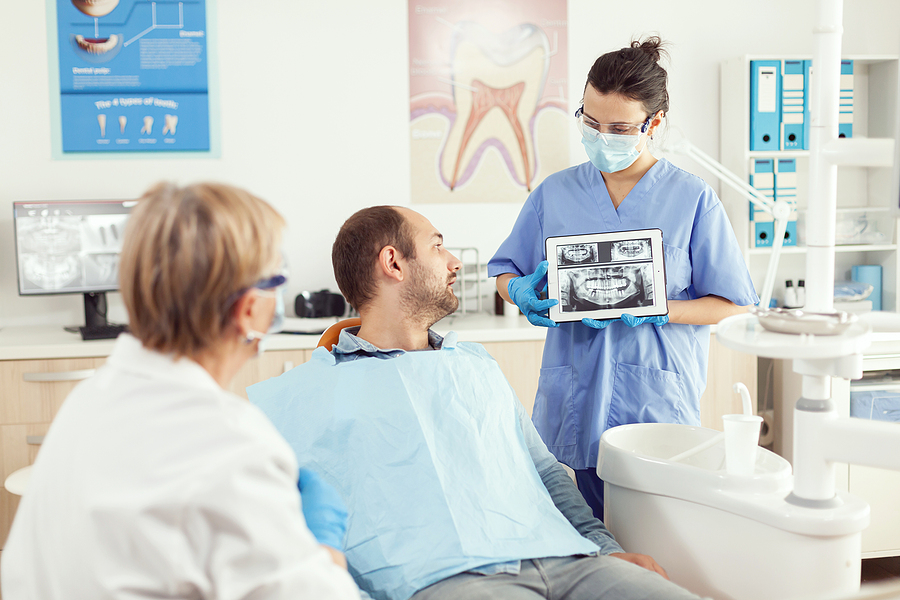
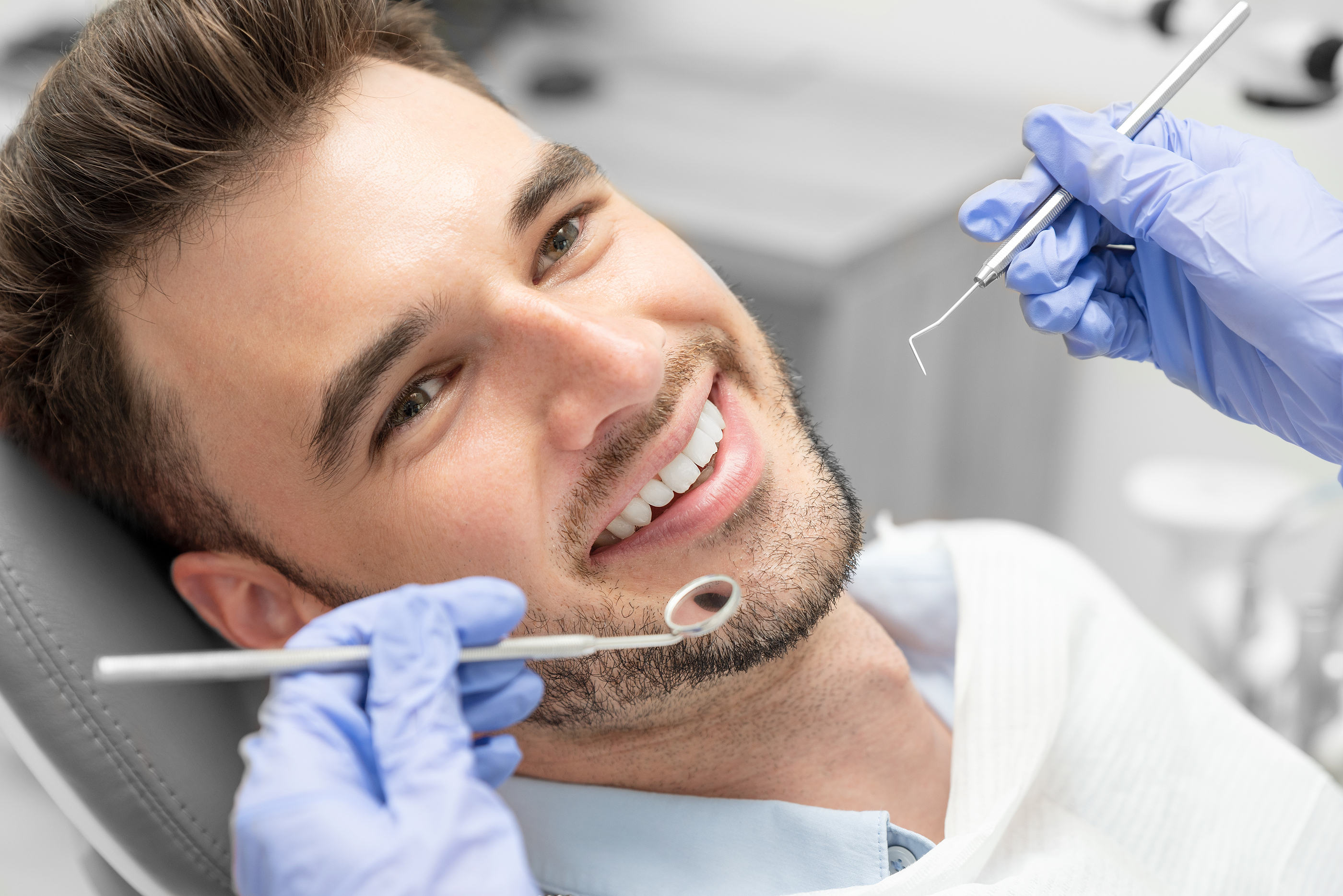
How is Gum Disease Diagnosed by the Dentist?
During a dental examination, we will look for the following things:
- Gum bleeding, swelling, stiffness, and pocket depth (the larger and deeper the pocket, the more severe the disease) are all factors to consider.
- Tooth sensitivity and movement, as well as appropriate teeth alignment
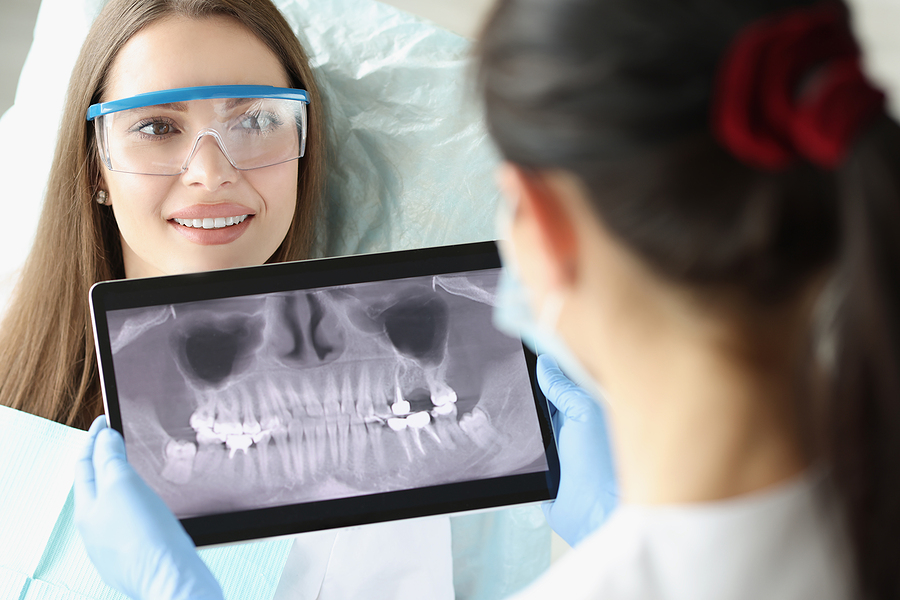
- Dental X-rays can be used to detect bone loss around your teeth.
Gum Disease Treatment
Scaling and root planing are the first operations we prescribe for treating gum disease. Scaling is the process of removing all of the plaque and tartar that have accumulated above and below the gum line. The ultrasonic device used dislodges the tartar deposits, and the debris is then washed away with a jet of water. Root planing is the process of smoothing rough surfaces on teeth to prevent tartar or food particles from forming. In some cases, medications and surgery can be used depending on the severity of the condition.
Please reach out to Persimmon Dental Care in Dublin, CA, to have a consultation with our dentists. Please call us at (925) 999-8282 or schedule an online consultation, and we’ll guide you further.
Periodontal Treatment
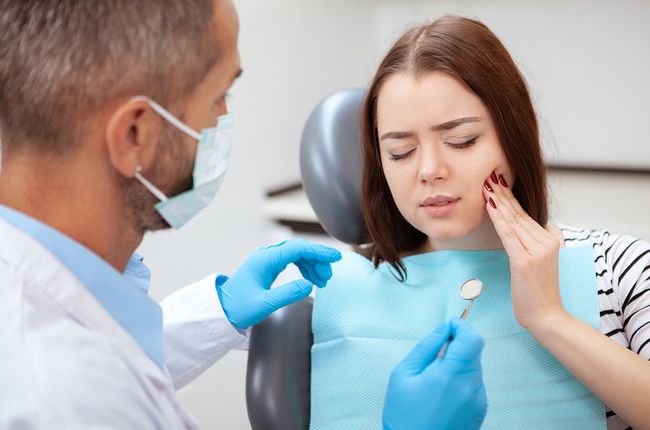
Periodontal diagnosis
Sedation Dentistry
Laser Dentistry

Early Orthodontic Treatment

What’s the Best Toothpaste for My Child?
Sealing Out Tooth Decay

Good Diet
How can fluoride prevent tooth decay?

Care for Your Child’s Teeth

First Visit

How Often Should Children Have Dental Checkups?
When Should Children Have Their First Dental Visit?
Office Hours
MON - FRI 9:00 am - 6:00 pm
SAT - SUN Closed